Agentless Process Servers
A normal configuration for running native OS processes consists of two separate parts:
-
A Process Server in the central Redwood Server system, where OS jobs are represented by processes.
- A Platform Agent on the computer where the OS processes run.
If you need to run native OS jobs on servers where you do not want to install or are not able to install a Redwood Server Platform Agent, you can do this by configuring an agentless Process Server.
Agentless operation is supported for UNIX and Microsoft Windows. It uses a proxy Platform Agent, which receives the OS job instructions and then forwards them on to the computer where the OS job will be executed. The proxy Platform Agent connects to the target server by means of SSH (UNIX) or WMI (Microsoft Windows).
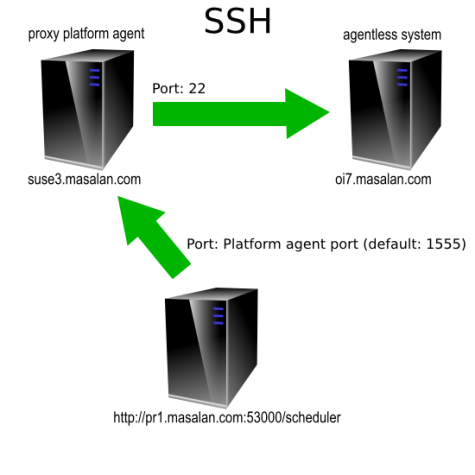
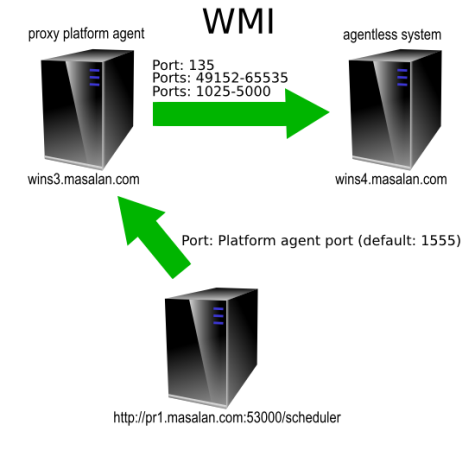
You must configure at least one normal UNIX Process Server and Platform Agent if you want to run agentless UNIX processes, and you must configure at least one normal Windows Process Server and Platform Agent if you want to run agentless Windows processes.
Prerequisites
A UNIX proxy Process Server must have an ssh client, and must be able to reach the target agentless server on port 22. Its target system requires an ssh server running on port 22.
Note: UNIX proxy Process Servers that use key-based SSH authentication are supported with no additional configuration.
A Windows proxy Process Server must have access to the target agentless system on RPC and WMI ports. Note that WMI uses port ranges. A temporary SMB network share will be created on the proxy Platform Agent and accessed on port 44.
Configuring the Process Server
To run OS jobs on a server, you must have one Process Server per host. Each Process Server must be configured with the following parameters in the Parameters tab.
| Parameter | Default Value | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Agentless | true
|
Set this to true to create an agentless Process Server. |
| RemoteHostName | The hostname of the server that the OS job will run on. | |
| ProxyProcessServers | An optional comma-separated list of Process Servers that can function as proxies. |
If the ProxyProcessServers field is empty, the list of valid proxy Process Servers is populated with the list of all non-agentless Process Servers that provide the Definition Type of the process. If ProxyProcessServers is NOT null, its value is used as the list. In either case, the first Process Server from the list that is running will be used as the proxy.
The following Process Server Parameters are supported for agentless Process Servers.
- RemoteHostName
- EndPoint
- LowVolume
- DefaultRunAsUser
- CygwinInstallPath (Windows only)
- LocalInterpreter_XXX
- InterpreterWhitelist_XXX
All other parameters either do not apply or have their values supplied by the proxy Process Server.
Special Considerations for UNIX Processes
If you want to run UNIX processes remotely, consider the following restrictions.
- The proxy server (with the Platform Agent) must possess an
sshclient. - The server that the OS job will run on must possess a working
sshserver (daemon). - If the Process Definition does not have a full set of credentials (username + password), the SSH connection will be tried using the username. If the username is not set, RunMyJobs will try the default user that OS jobs run as on the proxy host. In such cases, the system will use the
authorized_keysmechanism.
Special Considerations for Windows Processes
If you want to run Windows processes remotely, consider the following restrictions.
- The proxy server and the target server must both have WMI active and configured.
- Both servers must belong to the same domain, or there must be a trust relationship between the servers' domains.
- Each Process Definition must be fully authorized, including a password. Set the Run As User field to a username or domain\username, with either a password in the Run As User field or in a credential object.
- The user specified in the authorization must be an administrator account on the target server.
- Enable incoming WMI and DCOM connections in the firewall on the target server. If you use the built-in Windows Firewall, enable the following inbound rules on the target server:
- Windows Management Instrumentation (DCOM-In)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI-In)
- The proxy server must allow file sharing to the target server. As part of an OS job, a temporary network file share is created on the target server to the output and log files on the proxy server.
If you get a WMI connection failure, especially if accompanied by error code 0x800706ba, make sure you have created the firewall exceptions as indicated above. For more information, see System Administration > Windows Management Instrumentation > Using WMI > Creating WMI Clients > Connecting to WMI on a Remote Computer > Connecting Through Windows Firewall in the Microsoft MSDN documentation.
Implementation Details for Windows
This section shows how the agentless functionality is implemented on Windows and explains the requirements described above.
The proxy Process Server prepares a job-specific directory. Since all job directories and the files in it are to be owned by the Run As User, this user account must be known on the proxy Process Server. Even if it were owned by a different user. the actual OS runner account would have to be granted full access to these files, so there is no workaround for this restriction.
The proxy Process Server then accesses the target host via WMI. Microsoft Windows requires Administrator privileges to allow this. It also shares the proxy Platform Agent binary and data root directories via SMB. The latter requires no special privileges as it is performed by the local system account. You can see these network shares if you run 'net share' on the proxy Process Server. The following is example output.
C:\> net share
Share name Resource Remark
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
C$ C:\ Default share
IPC$ Remote IPC
ADMIN$ C:\Windows Remote Admin
agent-SystemID_10180-bin D:\agent\9_2_11_20230727_18\bin
agent-SystemIDs_10180-dataroot D:\agent\var\SystemID_10180\proxyhost
The command completed successfully.All actions on the WMI channel for a single job are bundled into one WMI session running as the same user. From Windows 2008 onwards, these sessions are fully isolated, even from other agentless jobs.
During the Dispatched phase of a process, the proxy job processor tries to access the target host's ADMIN$ share, in particular \\host\ADMIN$\Temp. This is the default system temp directory. The proxy job processor creates a temporary directory and stores a small executable and a log file there. If the creation of this temporary directory and the files succeeds, it is able to call the copied executable in order to create a temporary network share to \\proxyhost\agent-SystemId_port-dataroot with a temporary drive letter.
If the access to the ADMIN$ share fails, the proxy job processor runs NET USE directly. This has the disadvantage that it needs to pass the password in clear text, and cannot handle all possible punctuation characters in passwords. In particular, a password containing a single or double quote or a space may not function correctly on all Windows versions. You can either change the password or enable access to the ADMIN$ share on the target host.
Once the temporary drive has been set up, the job goes into the Running status. The job processor on the proxy host asks WMI to start a second copy of the job processor, but this time running on the target host. The job processor on the target host switches to the correct WoW (Windows On Windows) environment if a 64 bit execution environment is requested, and runs the CMD script or CMD shim. Because CMD is used for all Definition Types as a buffer to set up the correct environment for the process, it is required for all processes. Unfortunately, CMD requires a current directory that starts with a drive letter. This is why RunMyJobs must set up a temporary share for every job.
Once the user code is finished executing, the WMI session ends. This automatically cleans up the temporary network share access and drive letter on the target host. The job processor on the proxy host then removes the temporary directory in ADMIN$\Temp and copies any log files to the JobFiles directory. You can find these extra log files as extra files attached to the job.
stdsetup.logcontains the execution log of setting up the\\host\agent-SystemID_port-datarootshare.stdremote.logcontains the execution log of the actual job processor running on the remote Platform Agent.
Debugging Agentless Connections
When you run an agentless process, it is executed by calling remote (SSH or WMI) software from a job processor on the proxy server. A stdlog.log file is created by this job-processor jprocess. If you need to analyze the operation of the remote OS job creation, you must change the log level setting of the proxy Process Server, and not the target Process Server.
Configuring WMI Port Ranges or Static Ports
By default, WMI initially makes a call from the client server to the target server via RPC on port 135. Subsequent calls are then made on various ports in the range defined for WMI. The port ranges differ for the various supported Windows versions. For more information, see KB832017.