Product Release and Support Strategy
Redwood development works in agile continuous delivery mode.
In order to synchronize the releases and provide comprehensive versions to customers, Redwood decided to shift to a calendar-based versioning for all its products. The new version scheme is derived from the date of release using the YYYY.release format, with one service pack that includes enhancements and bug fixes every quarter of the year.
Version Numbering
Version numbering works as follows <year>.<service_pack>.<patch_level>.<hotfix>
|
|
Service Pack/Update | Patch Level/Patch | Hotfixes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | A new service pack may include both product enhancements and fixes. Redwood provides service packs for active major versions on a quarterly basis. | A patch includes only corrections to reported issues. Patches are made available for all service packs in the production phase as required. They don’t follow a regular schedule. more details | Hotfixes are incremental and not always publicly released. |
| Example version change |
2024.2 to 2024.3 |
2024.3.0 to 2024.3.1 |
2024.3.1.1 |
Active Version and Service Packs
Our development team provides enhancements and fixes to both the major and minor versions.
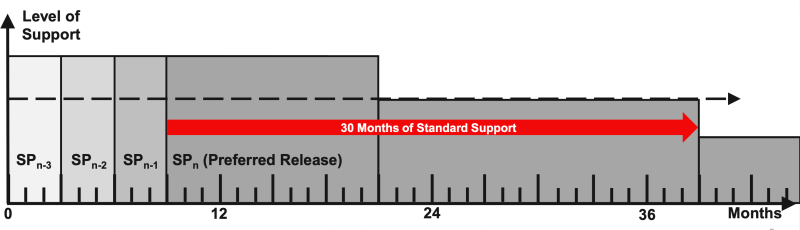
For active versions Redwood provides service packs (SP) every 3 months.
With an SP, only the second digit of the version changes (e.g. from 2024.1 to 2024.2). Redwood provides standard support for every SP for 30 months. After that, Redwood provides support at best effort.
Redwood adds enhancements only to the most recent SP, which is the preferred release.
SPs and patches are cumulative, so that the newest SP or patch includes all changes of the previous SPs and patches.
Redwood recommends updating to the latest SP at least once a year.
Lifecycle Phases and Level of Support for EACH Product Version / Service Pack
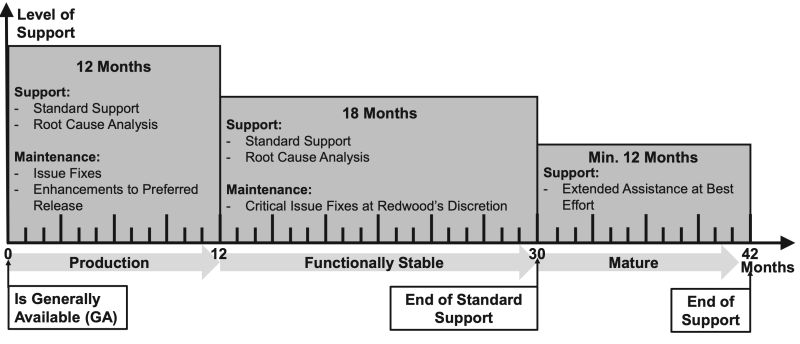
End-of-maintenance (EOM)
The end-of-maintenance date is defined as the point at which the software will no longer receive updates or bug fixes, but support will still be available to users. End-of-life happens 12 months after the release date, and notifications will be sent to users before that date.
Updates or patches for software applications that have reached their end-of-maintenance date will no longer be provided.
End-of-life (EOL) or End-of-support (EOS)
The end-of-support date is defined as the point at which the software will no longer be supported, and no further updates or bug fixes will be provided. End-of-support happens 18 months after the end-of-maintenance date as described in the documentation at the time of the release.
 On-premise: How to Install New Product Versions
On-premise: How to Install New Product Versions
You download all product versions directly from the support portal. In every product version, Redwood ships software as a whole to ensure that you can install new product versions with minimal risk and effort. Newer patch levels and/or service packs include all previous changes. This means that it only takes one update to get the latest SP version. The process of installing a new version is designed to be simple and have no impact on the objects stored in the underlying database.
When you install a new version, the installation process itself manages all product components and connected Platform Agents on remote systems. This ensures compatibility and rapid deployment, further reducing risk and required effort.
Updates vs. Upgrades
Updates and upgrades use the same technical method, however, upgrading less often has a bigger impact than frequent updates. A product update is usually fully automated. An upgrade from older versions may involve additional manual activities.
Redwood teams will suggest moving to a new major release when either:
-
The product version used has reached end-of-life and is no longer supported.
-
The release used by you no longer receives non-critical patches because it is deemed mature.
-
Key requirements can only be met with the new release.
 Product Release and Support Strategy for Software-as-a-Service
Product Release and Support Strategy for Software-as-a-Service
The Release strategy for our Software-as-a-Service solutions ensures continued support.
In addition to the normal service packs, security fixes and patch versions will be provided as required.
The Update process is completely automated including all Platform Agents, and customers can change the schedule of the update process within certain boundaries.
Upgrades are communicated to the General- Notifications/Reports contacts in the SaaS portal and made available on the dashboard.
Planning Service Packs
Up to four service packs can be released every year.
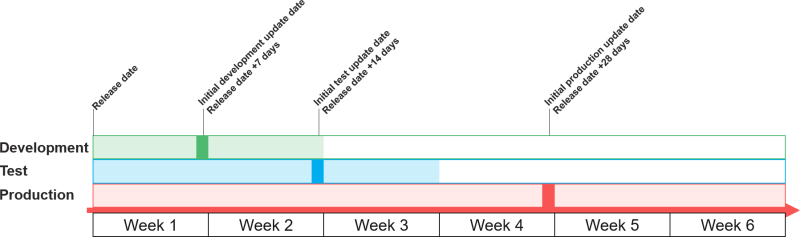
- After a release is made available the upgrade is planned per environment with an option to change
- Development 1 week after release (ability to postpone 1 week)
- Test 2 weeks after release(ability to postpone 1 week)
- Production 4 weeks after release(ability to postpone 2 weeks)
- It is always possible to perform an update earlier than planned
Planning RunMyJobs Service Packs

Planning Patches
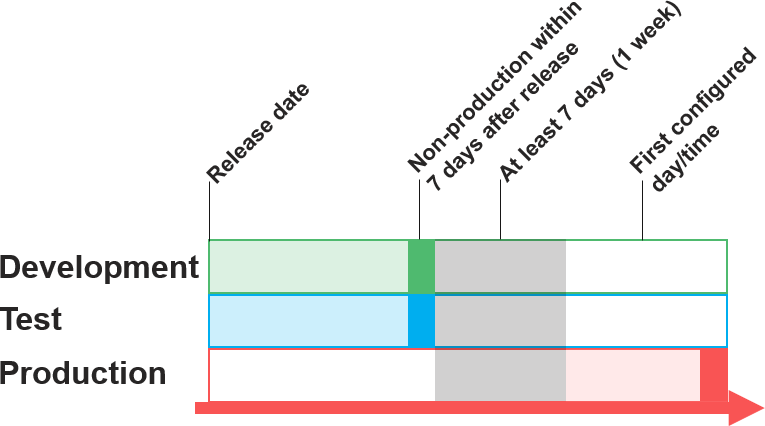
-
Environment administrators can set a patch window (day + time) for non-production and production
- Non-production will be done in the 1st week after release (no later than 7 days after release)
- There will then always be a 7-day period before production can be patched
- Production will then be scheduled at the next configured day/time (no later than 21 days after release)
-
Released patches will automatically roll out at the selected patch windows
-
Additionally, Redwood will have to do mandatory maintenance on the infrastructure, these do not contain product updates but might require a restart at a day/time defined by Redwood. This will be announced via message of the day and email.
Note: Patches consist of only bug fixes and/or security updates and are crucial to ensure the security and stability of the Redwood SaaS platform.
Tip: For Finance Automation environments you get the option to skip non-critical patches.
Update Process per Instance
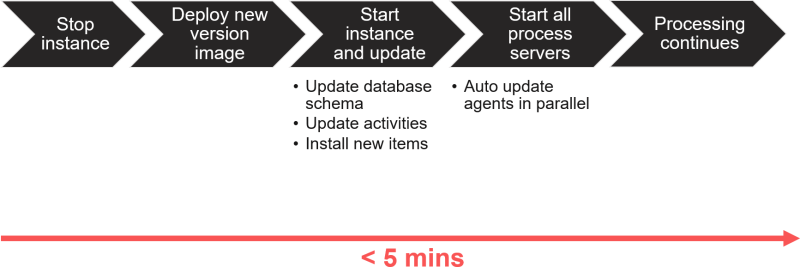
FAQ
Q1: Do I need to stop my Queues before an update?
A1: almost all Definition Types are resilient to system restarts. Only JDBC and Webservice calls are synchronous. RedwoodScript is by default also synchronous, but can be made resilient with the jcsJobContext.becomeResilient api call. So only for those processes you should stop the respective Queues in order to ensure that they do continue automatically after the update.
Q2: Are there other manual activities that need to take place after an update?
A1: There are no technical manual activities required. It is advised to validate the working of all components in the non-prod environments after an update to prevent surprises during the production update.