How Job Servers Work
To understand Job Servers, you need to understand how the various parts of Job execution fit together.
-
A Job Definition defines what a Job does.
-
A Queue determines when and where the Job Definition runs.
-
A Job Server is in charge of running the Job Definition.
-
A Service is a tool used by a Job Server to do the actual work. There are different Services for different kinds of work. For example, if you have a process that runs an Oracle job, it needs access to the OracleJobService.
Job Server Services
Each Job Server is associated with one or more specific Services. The Services assigned to a Job Server determine what kinds of Jobs that Job Server can run. So it is critical that each Job is routed to a Job Server that has the Service the Job needs.
This routing is accomplished via Queues. Each Queue is associated with one or more Job Servers. When you submit a Job Call, you submit it to a particular Queue. That Queue looks through its Job Servers to see if it has one with a matching Service. If it does, it sends the Job to that Job Server. If it doesn’t, the Job Call cannot execute.
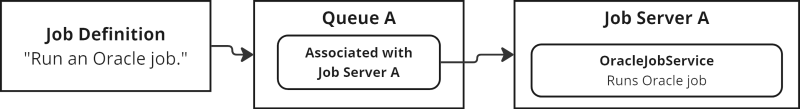
Some Job Definitions are designed to (for example) run scripts on client computers. For those Job Definitions, an additional piece is necessary.
-
A Platform Agent is software that runs on a computer inside the customer network and executes tasks on that computer.
To use a Platform Agent, a Job Server must be able to communicate with the Platform Agent that will execute the tasks. Consequently, the Job Server must be configured with a PlatformAgentService, which can talk to a Platform Agent.
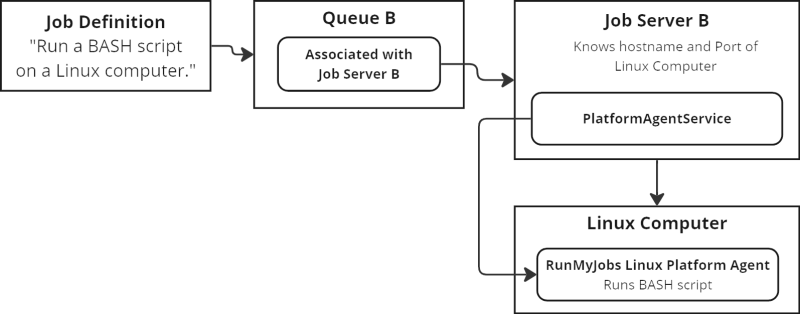
Job Server Definition Types
Each Service you associate with a Job Server can in turn be associated with one or more Definition Types. Each Definition Type provides a capability to the Service. For example, if you add a PlatformAgentService to a Job Server (as in the above diagram), it may have options for several Definition Types, each representing a type of operation the Platform Server can perform with a Platform Agent.
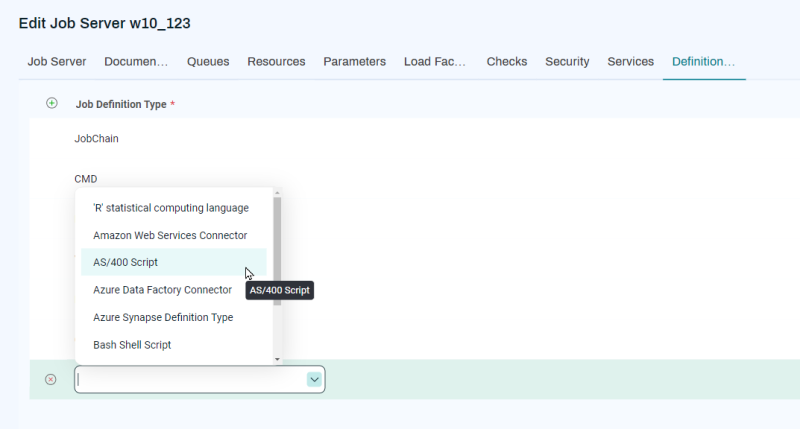
If you create a Linux, UNIX, or Windows Platform Job Server, the PlatformAgentService is automatically added to the Job Server. You can then choose which particular Definition Types you want that Platform Job Server to support.
If you create a Job Definition that uses a particular scripting language (for example, CMD), you need a Job Server that has the CMD Definition Type selected.