About Queues
RunMyJobs uses Queues to manage groups of Jobs. Queues distribute Jobs to Job Servers, where the Jobs actually run. You can use Queues to limit the number of Jobs that can run simultaneously, distribute workload across multiple systems, and provide fail-over facilities.
RunMyJobs provides a standard Queue named System. You cannot change or hold this Queue, so you will most likely need to create your own Queues.
Note: Redwood recommends that you specify a time zone on a Queue to make sure the correct time is used, especially if you tie it to a Time Window to it.
Queues and Job Servers
A Queue can be served by more than one Job Server, and a Job Server can be associated with multiple Queues.
-
You can link a Queue to a Job Server by creating a Queue Provider in the Queues tab for the Job Server.
-
You can link a Job Server to a Queue in the Job Servers tab for the Queue.
Queue Providers
The way to associate a Queue with a Job Server is to add a Queue Provider to that Job Server. A Queue Provider specifies the following things:
-
A reference to a specific Queue.
-
Whether the Queue should be initially held.
-
An execution size for the Queue.
-
A hold level.
-
An optional Time Window and time zone.
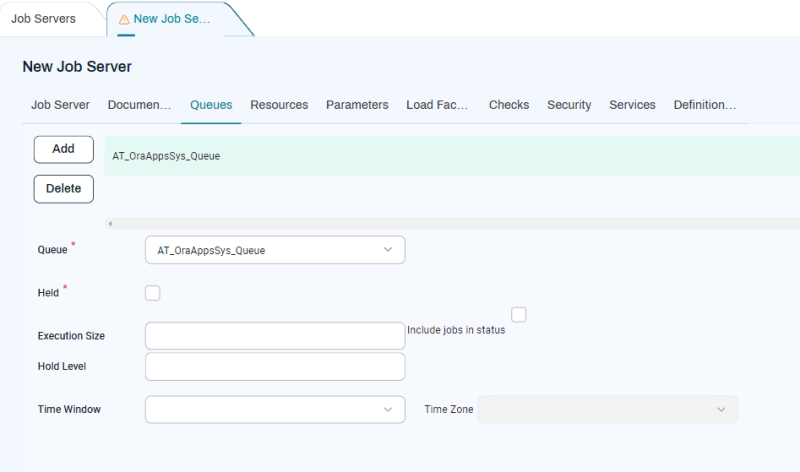
You can add Queue Providers to a Queue by going to its Queue Providers tab.
Queue Restrictions
A Job that needs to be executed waits in a Queue until a Job Server that (a) serves that Queue, and (b) provides the required Resources is available. In addition, such Jobs are subject to Queue limits. For example, a Queue's Time Window can restrict it from executing Jobs during certain times. Queue Providers can also have restrictions.
If a Queue has multiple restrictions, he most restrictive setting applies. For example, assume a Queue has an Execution Size of 3. If a Queue Provider serving this same Queue has an execution size of 6, this latter value is never reached. Similarly, if the Time Window of a Queue Provider is always closed during the Time Window of the Queue, the Job Server will not run any Jobs from that Queue.